Every seasoned digital marketer knows that Google has made a habit of updating its methods, policies, and search algorithms practically every year. The BERT and SMITH updates are the latest additions to Google’s search technology innovations.
While Google introduced BERT in 2019 and followed it up with SMITH 2021, both these algorithms are centered around Google’s understanding of search queries. These updates will not just improve internet users’ overall search experience. They are also crucial to online businesses, especially those that depend on search results as their primary source of traffic.
This piece will thoroughly explain both of these new algorithms, and outline the various ways the changes can benefit local businesses. I’ll also discuss how the updates affect online searches.
The BERT & SMITH updates
Before discussing these algorithms individually, it’s good to understand how they work together. Since they have more similarities than differences, there is some value in discussing what BERT and SMITH have in common and how they are related to each other.
In the last decade, Google has poured increasing amounts of resources into natural language processing (NLP) models for use primarily in its search engine. Both SMITH and BERT are rooted in NLP, which enhances the way Google understands, processes, and answers search queries.
What is the BERT algorithm?
When Google implemented BERT in 2019, it estimated that the update will enhance around 10% of queries. More importantly, however, the search giant also predicted that the scope of this change would also cover organic rankings for online businesses of all kinds.
BERT stands for Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers. The name is associated with the research on language processing carried out by Google, as well as the resulting algorithm.
In its simplest form, BERT helps Google understand the meaning of words in a sentence by considering various factors, such as tone and context, that add nuance to it.
The problems of homophones and prosody (rhythm, stress, and intonation) also fall under the scope of BERT. For instance, the phrase “four candles” might be pronounced as “fork handles” by a person with an English accent. BERT seeks to use context in these kinds of scenarios to narrow down the search results to what it perceives as relevant.
Using BERT, Google can better match search queries from users with more relevant, helpful results. Words, phrases, and sentences can be ambiguous at times. The BERT algorithm update helps Google figure out the search intent behind queries which can confuse human listeners.
What is the SMITH algorithm?
In late 2020, Google published yet another paper on natural language processing. The paper introduced a new NLP algorithm called SMITH, which overcomes some of the shortcomings of the BERT update.
In many ways, the SMITH update was introduced as an improvement on the BERT algorithm. In fact, it has already been reported to outperform BERT in a plethora of key scenarios. According to industry reports, this new algorithm has already shown the capacity to understand long-form content and queries better than its immediate predecessor.
SMITH improves on the processing power of its predecessor. It has a considerable amount more bandwidth, increasing the speed and efficacy at which it works.
However, if it boasts an exponential improvement over its predecessor, SMITH still relies on many of BERT’s underlying processes to function. While BERT would screen every word to glean meaning, SMITH utilizes batch processing to speed up the process.
How can businesses benefit from the updates?
In discussing the potential benefits of these changes to local businesses, it’s best to see both these algorithms as two related pieces in the search puzzle. Since SMITH is an improved iteration of BERT, these benefits can be discussed in relation to both of the algorithms simultaneously.
Here are a few key SEO benefits to local businesses from the BERT and SMITH Google algorithm updates.
More Opportunities for Longer Form Content
Beginning with BERT, Google identified a pressing need for its search algorithms to be able to better understand long-form content. A better understanding of content enables Google to consider passages within the context of an article.
Google uses those insights when providing its instant answers. You can see how it does this for an article targeting the term “hunter alternatives.” Check out the image below to see what I mean.
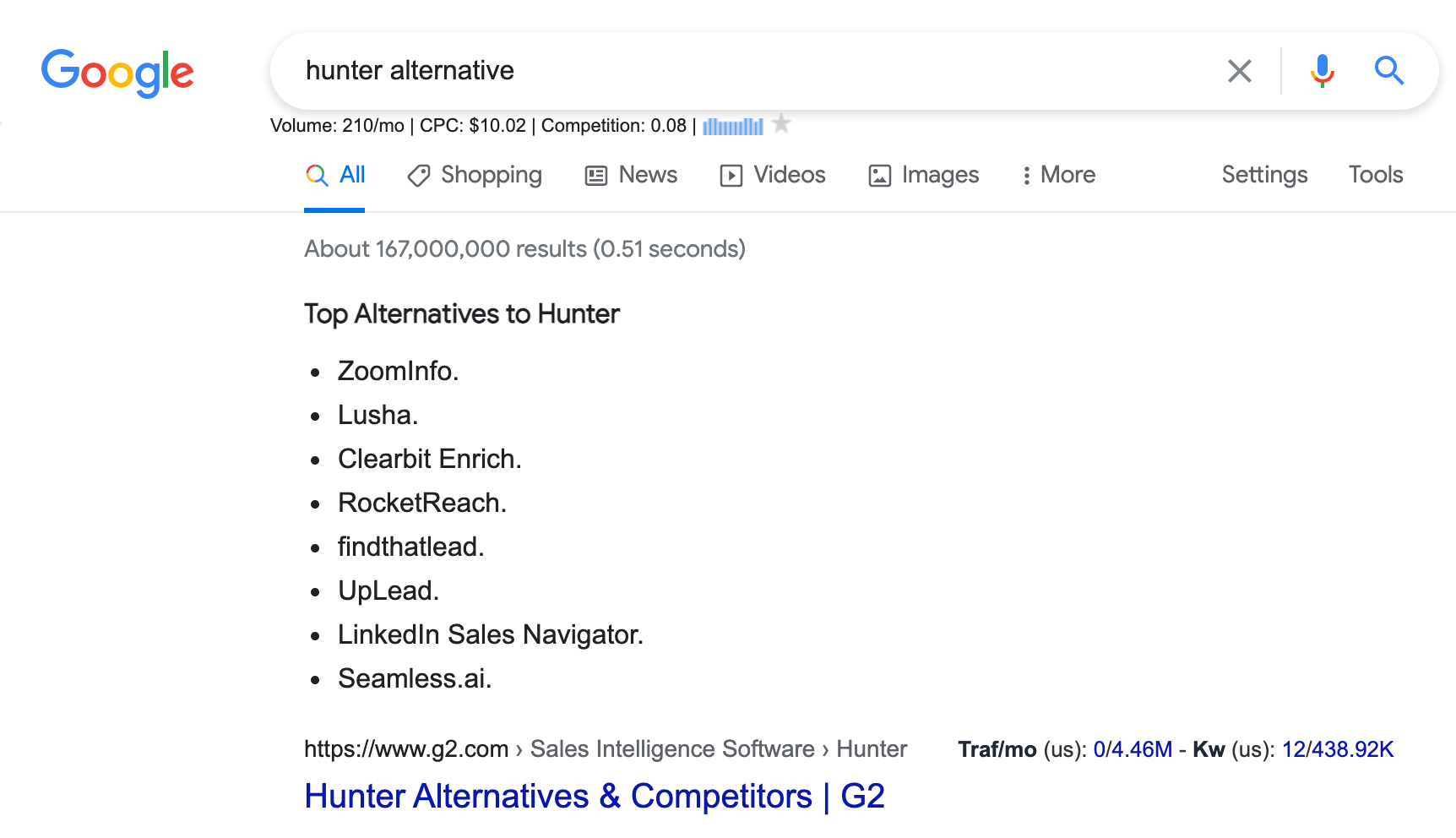
From the search and the indexing side of things, these updates allow users to find more precise matches for their search queries.
The ability of Google to better understand longtail queries is a profound marketing and customer service opportunity. As a savvy SEO, you can take advantage of these changes to boost your rankings by incorporating relevant terms, and answers to questions in your content.
Google Indexing Passages in Content
Following the SMITH update, Google announced in October 2020 that it would begin passage-based indexing for the English language. This development has been around for a short while now and, while many users might not have clocked its existence, it is an integral part of the new age of search.
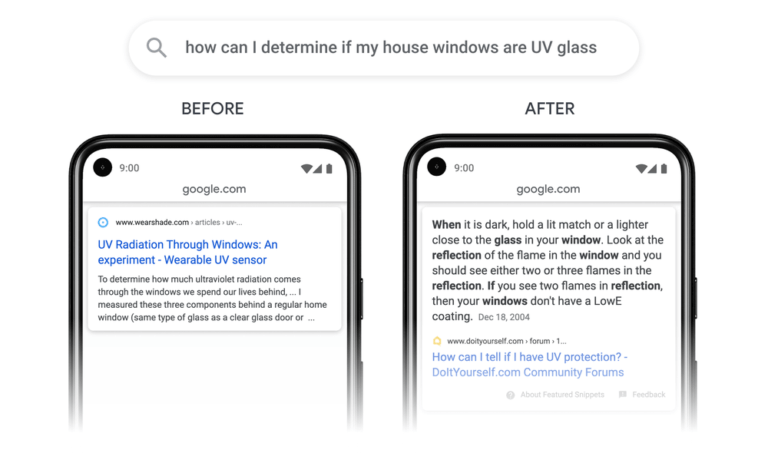
Google brought up the need for a passage-based indexing mechanism as it sought to limit the number of clicks and scrolls it would take a user to reach the results of their query. This feature is especially useful for direct questions where the answers to the search question are buried deep in a 2,000-word article.
Google indexes the right passage from the source website and - as we can see from the photo above - shows the direct answer to the searcher alongside the clickable H1 title tag of the website.
This new development is a game-changer that will reward local businesses that put the user first. Google itself is showing discernible attention to searchers and, therefore, if you want to rank better, you need to optimize less for google and more for your audience.
Customers want to make sure that your product or service answers their pain points. Having passages indexed from your content as relevant answers is a great way to attract traffic. After all, if your content was good enough to get featured in a Google search, your brand and products must be pretty good too.
Let’s make this clear: Google isn’t going to index individual passages instead of your website or content page as a whole. However, it will zero in on search-relevant passages as it decides whether or not to rank your page for specific queries. If your content answers a question, it is likely to show up in the results. How high it will rank, though, will still depend on other factors, such as domain authority, traffic, and keyword density.
Wrapping up
Google search is in a constant state of flux, and as an SEO practitioner, you need to understand how the changes to its search algorithm affect the way human users search for information and how it also affects the search rankings. Google continues creating search algorithms that rely heavily on machine learning to mimic how humans ask questions and give answers.
Because the new algorithm leans heavily towards long-tail keywords, it opens a lot of opportunities for businesses to optimize their content for local searches. Not only will Google recognize local searches and look for relevant pages more effectively, but the suggested results themselves will also be more oriented towards locally published content.
Along with the new BERT and SMITH updates, search results are evolving. It’s about time your local SEO should evolve with them too.
 Members Area
Members Area